Google Tag Manager (GTM)
In the current digital world, making decisions based on data is important for businesses who wish to maintain their competitive edge. To accurately monitor user interactions, analyze website performance, and implement effective marketing strategies, a strong analytics setup is necessary. This is where Google Tag Manager (GTM) can be of great help. GTM is a powerful tool that streamlines the management and implementation of various tracking codes and tags on your website. In this article, we will delve into the features, advantages, and best practices of utilizing GTM to improve your tracking and analytics efforts.
What is Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
Google Tag Manager is a free tag management system developed by Google. It allows marketers and website administrators to easily manage and deploy various tags and tracking codes without requiring direct access to the website’s source code. Instead of manually adding code snippets to each page, GTM provides a user-friendly interface where tags can be configured and published with a few clicks.

Key Features of Google Tag Manager:
- Tag Management: GTM simplifies the process of managing tags from different platforms, such as Google Analytics, Google Ads, Facebook Pixel, and many others. It centralizes the management of these tags in one place, making it easier to add, edit, or remove them as needed.
- Code Deployment: With GTM, you can deploy code snippets or tags across your website without the need for manual coding. This eliminates the dependency on developers for tag implementation, enabling marketers to quickly launch tracking and marketing campaigns.
- Version Control: GTM includes a version control system that allows you to make changes to your tags and revert to previous versions if needed. This feature helps to avoid accidental changes and provides a convenient way to manage updates and rollbacks.
- Preview and Debug: GTM provides a built-in preview mode that allows you to test and validate tags before publishing them live. The debug console enables you to troubleshoot any issues with your tags and ensure they are functioning correctly.
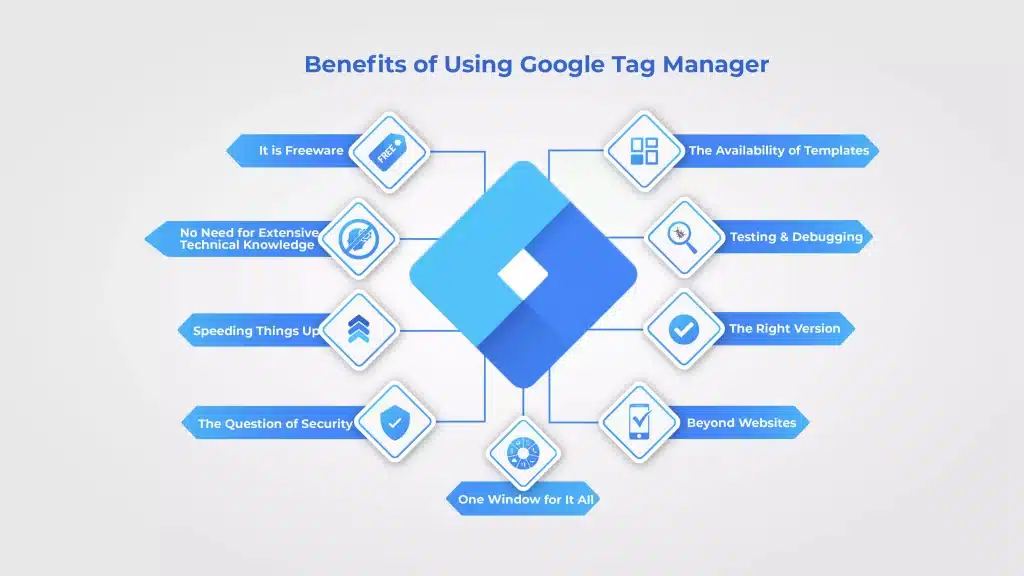
Benefits of Using Google Tag Manager:
Simplified Workflow: GTM streamlines the process of implementing and managing tracking codes. With its intuitive interface, you can easily add, edit, or remove tags without relying on developers. This saves time, improves efficiency, and reduces the risk of errors.
Increased Agility: Traditional tag implementation requires manual changes to the website’s source code, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. GTM’s code deployment capabilities empower marketers to launch campaigns faster, respond to market changes swiftly, and iterate on their tracking strategies without delays.
Enhanced Tracking Flexibility: GTM offers advanced features like triggers and variables that allow you to customize and fine-tune your tracking setup. You can define specific conditions for firing tags based on user interactions, such as button clicks, form submissions, or scroll depth. This level of flexibility enables you to capture more precise data and gain deeper insights into user behavior.
Collaboration and Control: GTM provides a user management system that allows multiple team members to collaborate on tag management. You can assign different levels of permissions to control who can create, edit, or publish tags. This facilitates teamwork, improves accountability, and ensures proper oversight of tag implementation.
How Does Google Tag Manager Work?
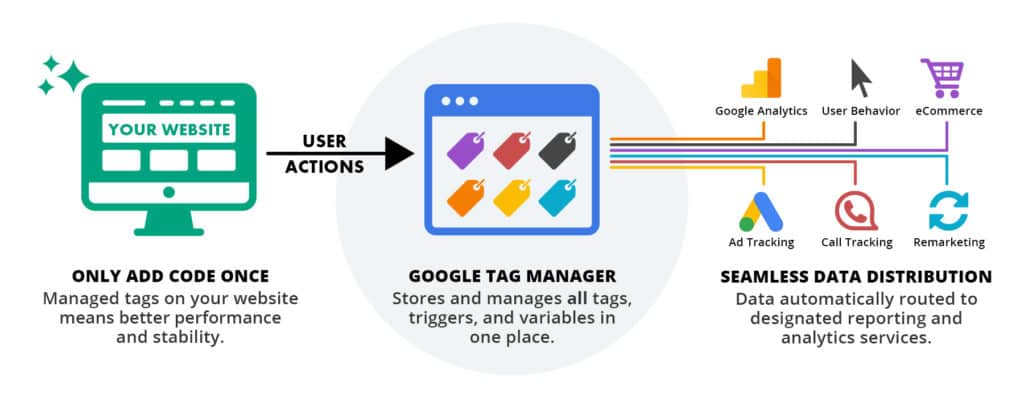
To manage tags on your website, you can use Google Tag Manager by simply adding a single JavaScript code snippet as a container. This will allow you to manage all the tags you need more efficiently.
When a user triggers a tag (e.g., by clicking a link or loading a page), GTM retrieves it and injects it into your website code. Then, GTM executes the tag.
To put it simply, GTM will only add and carry out a tag if it is activated by a user. This helps to decrease the amount of code on a website and lowers the chance of any mistakes during implementation.
Tags work with other GTM components called triggers and variables to determine when to execute code snippets.
What are Tags?
Tags refer to small pieces of code that are utilized by analytics, marketing, and support platforms to integrate with sites and applications. For instance, Google Analytics employs tags to gather data on website visitors. In this scenario, the Google tag enables you to transmit data from your site to a linked Google Analytics property. With the aid of GTM, you can generate, oversee, and release tags without the need to write code yourself.
What are Triggers?
Triggers are instructions that determine when tags should be activated. Examples of triggers include page views, form submissions, and link clicks. When a user performs any of these actions, the corresponding tag is activated. It is essential to assign a trigger to each tag so that the Tag Manager can activate the tag under the appropriate circumstances.
Best Practices for Using Google Tag Manager:
Develop a Tag Management Strategy: Before diving into GTM, establish a clear strategy for your tracking and analytics goals. Define the key metrics you want to measure, the tags required to track them, and the events that trigger those tags. This strategic approach will help you organize your tags efficiently and maintain a clean and manageable GTM container.
Test Tags Before Publishing: Always use the preview mode and debug console in GTM to verify that your tags are working as intended. Test different scenarios and user interactions to ensure accurate data collection. This practice helps to prevent data discrepancies and allows you to identify and fix issues before they impact your analysis.
Document and Organize Your Tags: As your tracking setup grows, it’s crucial to maintain proper documentation and organization within GTM. Use descriptive names and labels for your tags, triggers, and variables. Document the purpose and configuration details of each tag to facilitate future changes or handovers.
Regularly Audit Your Tags: Conduct periodic audits of your GTM container to ensure its cleanliness and efficiency. Remove any unused or redundant tags, triggers, or variables. Review and update your tracking strategy based on changes in your website or marketing campaigns.
Google Tag Manager is a valuable tool for marketers and website administrators to manage tracking and analytics effectively. It simplifies the process of deploying and managing tags, enhancing workflow efficiency, increasing agility, and providing flexibility in tracking customization. Following best practices and using the advanced features of GTM can help businesses gain deeper insights, make data-driven decisions, and optimize their online presence for success in the digital world.

bm42yv
gkwkfx
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
z1k8mz
kamagra pas cher: Acheter Kamagra site fiable – Kamagra pharmacie en ligne
https://pharmafst.com/# pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale
cialis sans ordonnance: Cialis en ligne – Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne tadalmed.shop
Achetez vos kamagra medicaments achat kamagra kamagra gel
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale: Medicaments en ligne livres en 24h – Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe pharmafst.com
68y3a6
cialis generique: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
cialis generique: Cialis generique prix – Cialis en ligne tadalmed.shop
https://tadalmed.shop/# cialis sans ordonnance
kamagra gel Kamagra pharmacie en ligne kamagra livraison 24h
Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie: Cialis sans ordonnance pas cher – cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
Kamagra Commander maintenant: kamagra oral jelly – Achetez vos kamagra medicaments
https://tadalmed.shop/# cialis generique
pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es: pharmacie en ligne pas cher – vente de mГ©dicament en ligne pharmafst.com
kamagra en ligne Kamagra pharmacie en ligne kamagra pas cher
acheter kamagra site fiable: kamagra pas cher – Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher
kamagra 100mg prix: achat kamagra – kamagra oral jelly
http://kamagraprix.com/# Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher
Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable Pharmacie Internationale en ligne vente de mГ©dicament en ligne pharmafst.shop
acheter kamagra site fiable: Acheter Kamagra site fiable – kamagra livraison 24h
pharmacie en ligne france livraison belgique: Meilleure pharmacie en ligne – Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe pharmafst.com
https://tadalmed.com/# Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance
п»їpharmacie en ligne france: Livraison rapide – trouver un mГ©dicament en pharmacie pharmafst.com
kamagra pas cher: Acheter Kamagra site fiable – Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher
Acheter Cialis Cialis sans ordonnance 24h Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne tadalmed.com
Acheter Kamagra site fiable: achat kamagra – kamagra pas cher
http://tadalmed.com/# Tadalafil achat en ligne
kamagra livraison 24h: kamagra gel – kamagra gel
Cialis en ligne: Acheter Cialis – Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
achat kamagra Acheter Kamagra site fiable achat kamagra
kamagra livraison 24h: kamagra pas cher – Acheter Kamagra site fiable
http://pharmafst.com/# pharmacie en ligne
cialis generique: Cialis sans ordonnance 24h – Cialis sans ordonnance pas cher tadalmed.shop
kamagra gel: kamagra pas cher – kamagra gel
Cialis sans ordonnance pas cher cialis prix Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.com
https://tadalmed.com/# Achat Cialis en ligne fiable
cialis sans ordonnance: Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance – Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
Achetez vos kamagra medicaments: Kamagra pharmacie en ligne – kamagra pas cher
Acheter Kamagra site fiable: Achetez vos kamagra medicaments – kamagra pas cher
Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie: Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie – Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher tadalmed.shop
pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance Pharmacie en ligne France pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale pharmafst.shop
http://kamagraprix.com/# Kamagra Commander maintenant
Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher: Achetez vos kamagra medicaments – Kamagra pharmacie en ligne
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: Tadalafil achat en ligne – cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
https://tadalmed.com/# Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance
vente de mГ©dicament en ligne: pharmacie en ligne – pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale pharmafst.com
https://tadalmed.com/# Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher
achat kamagra: achat kamagra – Acheter Kamagra site fiable
http://tadalmed.com/# Cialis generique prix
kamagra en ligne: kamagra oral jelly – kamagra livraison 24h
https://tadalmed.com/# Cialis en ligne
acheter kamagra site fiable: Kamagra pharmacie en ligne – Acheter Kamagra site fiable
kamagra pas cher: achat kamagra – kamagra gel
kamagra gel: Acheter Kamagra site fiable – Acheter Kamagra site fiable
acheter kamagra site fiable: kamagra livraison 24h – kamagra gel
Kamagra pharmacie en ligne achat kamagra achat kamagra
http://tadalmed.com/# Tadalafil achat en ligne
Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – Cialis generique prix tadalmed.shop
d6ijlv
pharmacie en ligne: Meilleure pharmacie en ligne – pharmacie en ligne livraison europe pharmafst.com
Tadalafil 20 mg prix en pharmacie: Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance – Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
http://pharmafst.com/# pharmacie en ligne france fiable
Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe Pharmacies en ligne certifiees pharmacie en ligne france pas cher pharmafst.shop
Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe: Pharmacies en ligne certifiees – pharmacie en ligne france fiable pharmafst.com
pharmacie en ligne: Pharmacies en ligne certifiees – pharmacie en ligne france fiable pharmafst.com
https://medicinefromindia.shop/# Medicine From India
RxExpressMexico: mexico drug stores pharmacies – RxExpressMexico
canadapharmacyonline com: Express Rx Canada – canada rx pharmacy world
canada drugs online reviews: Express Rx Canada – canadian pharmacy meds review
indian pharmacy MedicineFromIndia mail order pharmacy india
http://medicinefromindia.com/# MedicineFromIndia
medicine courier from India to USA: indian pharmacy online – indian pharmacy online
indian pharmacy online: MedicineFromIndia – indian pharmacy
mexican online pharmacy: mexican rx online – mexico drug stores pharmacies
http://medicinefromindia.com/# MedicineFromIndia
indian pharmacy online medicine courier from India to USA medicine courier from India to USA
canadian online pharmacy reviews: Express Rx Canada – canada pharmacy online legit
trusted canadian pharmacy: Buy medicine from Canada – canadian pharmacy cheap
canadian compounding pharmacy: Buy medicine from Canada – canadianpharmacyworld com
https://expressrxcanada.shop/# ed meds online canada
indian pharmacy online shopping: indian pharmacy – Medicine From India
Rx Express Mexico п»їbest mexican online pharmacies Rx Express Mexico
mexico drug stores pharmacies: RxExpressMexico – mexican rx online
RxExpressMexico: Rx Express Mexico – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
https://medicinefromindia.shop/# indian pharmacy online
indian pharmacy: indian pharmacy – buy medicines online in india
onlinepharmaciescanada com Buy medicine from Canada canadian pharmacy oxycodone
canada online pharmacy: Canadian pharmacy shipping to USA – legal to buy prescription drugs from canada
Medicine From India: Medicine From India – MedicineFromIndia
https://rxexpressmexico.com/# mexico drug stores pharmacies
indian pharmacy online: indian pharmacy online – indian pharmacy
Rx Express Mexico mexican rx online mexican online pharmacy
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs: RxExpressMexico – mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
https://rxexpressmexico.shop/# Rx Express Mexico
legal canadian pharmacy online: canadian world pharmacy – legit canadian pharmacy online
Medicine From India: indian pharmacy online shopping – indian pharmacy online shopping
medicine courier from India to USA: indian pharmacy online shopping – indian pharmacy
mexico drug stores pharmacies mexican online pharmacies prescription drugs mexican online pharmacy
http://rxexpressmexico.com/# mexico pharmacy order online
medicine courier from India to USA: medicine courier from India to USA – indian pharmacy online
MedicineFromIndia: indian pharmacy – indian pharmacy
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs Rx Express Mexico mexico pharmacy order online
http://rxexpressmexico.com/# mexico pharmacies prescription drugs
Rx Express Mexico: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexico pharmacy order online: mexico drug stores pharmacies – RxExpressMexico
mexican rx online: mexico pharmacy order online – mexico drug stores pharmacies
http://pinupaz.top/# pin up azerbaycan
пин ап казино официальный сайт пинап казино пин ап зеркало
pin up вход: пин ап казино – pin up вход
пинап казино: pin up вход – пин ап зеркало
http://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada casino
pin up casino: pin up azerbaycan – pin up casino
пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап казино официальный сайт пин ап казино официальный сайт
vavada: vavada – вавада зеркало
http://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada
pin up az: pin up – pin up az
вавада: vavada вход – вавада казино
pin-up pin-up casino giris pin-up casino giris
http://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada
пинап казино: пинап казино – пин ап вход
пин ап зеркало: пин ап зеркало – пин ап зеркало
pin-up casino giris pin up azerbaycan pinup az
http://pinupaz.top/# pin up
pin up: pin up azerbaycan – pin up azerbaycan
pin-up casino giris: pin-up casino giris – pin up az
pin-up: pinup az – pin-up
пинап казино пин ап зеркало pin up вход
http://vavadavhod.tech/# вавада казино
пинап казино: пин ап зеркало – пин ап вход
pin up вход: пинап казино – пин ап казино
vavada вход: вавада официальный сайт – вавада официальный сайт
vavada: vavada – вавада официальный сайт
http://pinuprus.pro/# пинап казино
vavada: вавада официальный сайт – vavada casino
vavada casino: вавада – vavada casino
pin-up casino giris pin-up pin up az
pin up вход: пин ап казино – pin up вход
пин ап зеркало: пин ап казино официальный сайт – пин ап казино официальный сайт
пин ап зеркало: пин ап вход – пинап казино
http://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada
pin up azerbaycan: pin up casino – pinup az
pin up: pin up azerbaycan – pin-up
http://pinupaz.top/# pinup az
pin up azerbaycan pin up az pin-up casino giris
вавада: vavada casino – вавада официальный сайт
vavada casino: vavada – vavada вход
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино официальный сайт
vavada вход вавада зеркало vavada casino
vavada: vavada casino – vavada
pin-up casino giris: pin-up casino giris – pin up
http://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап зеркало
вавада зеркало: вавада казино – vavada вход
пинап казино пинап казино пин ап зеркало
pin up вход: пин ап казино официальный сайт – пинап казино
https://pinupaz.top/# pin-up casino giris
вавада: vavada вход – vavada casino
pinup az pin up az pin-up
pin up: pin up az – pin-up
https://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada вход
pin up: pinup az – pin-up
pin up azerbaycan pin up pinup az
pin up azerbaycan: pin up azerbaycan – pin up casino
https://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada вход
vavada vavada casino вавада
pin up: pin up casino – pin-up
vavada: вавада – vavada вход
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап зеркало
пин ап казино официальный сайт пинап казино пин ап казино
vavada вход: vavada – vavada casino
pin up: pinup az – pin up
https://vavadavhod.tech/# vavada
пинап казино: pin up вход – пин ап вход
http://pinuprus.pro/# пинап казино
pinup az: pin up az – pin-up
vavada: вавада – вавада
pin up вход pin up вход пин ап казино
https://pinuprus.pro/# пинап казино
пин ап вход: пин ап зеркало – пин ап казино официальный сайт
pin-up casino giris: pin up – pin up
https://pinupaz.top/# pin up az
pin up вход pin up вход пин ап казино официальный сайт
пинап казино: pin up вход – pin up вход
пин ап вход: пин ап вход – пин ап казино
http://pinupaz.top/# pin-up casino giris
pin up casino: pin up casino – pin-up casino giris
пин ап казино: пин ап вход – pin up вход
http://pinupaz.top/# pin-up
pin up вход пин ап вход пин ап вход
вавада казино: vavada – вавада зеркало
вавада казино: вавада официальный сайт – вавада казино
http://pinuprus.pro/# пинап казино
вавада зеркало вавада vavada casino
вавада: вавада казино – вавада
vavada вход: vavada casino – вавада официальный сайт
https://pinuprus.pro/# пин ап казино официальный сайт
peptide tadalafil reddit: cialis for sale in toront ontario – free cialis samples
what does cialis cost TadalAccess can you purchase tadalafil in the us
buying cialis internet: price comparison tadalafil – cialis next day delivery
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy tadalafil no prescription
cialis headache: TadalAccess – cialis online with no prescription
cialis company Tadal Access buy cialis canada paypal
u.s. pharmacy prices for cialis: when should i take cialis – buy cialis no prescription overnight
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis 5 mg price
tadalafil citrate: cheap canadian cialis – what cialis
cialis prices tadalafil generic reviews cialis drug
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis canadian
cialis buy without: cialis generic – cialis premature ejaculation
cialis price cvs: TadalAccess – sildenafil vs tadalafil which is better
cialis tablet TadalAccess what are the side effect of cialis
https://tadalaccess.com/# teva generic cialis
cialis and dapoxetime tabs in usa: where can i buy cialis online in australia – cialis with dapoxetine 60mg
tadalafil tablets erectafil 20: buy cialis online canada – cialis ingredients
difference between sildenafil tadalafil and vardenafil Tadal Access cialis online canada ripoff
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis and melanoma
is cialis covered by insurance: tadalafil tablets – cialis 20 mg duration
cialis free trial voucher: Tadal Access – cialis online pharmacy
https://tadalaccess.com/# too much cialis
cialis price costco Tadal Access when does the cialis patent expire
where can i buy cialis over the counter: Tadal Access – cialis active ingredient
over the counter cialis walgreens: cialis samples – tadacip tadalafil
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis canada online
best place to buy generic cialis online Tadal Access buy cheapest cialis
tadalafil 5mg once a day: Tadal Access – original cialis online
who makes cialis: TadalAccess – cialis vs tadalafil
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis trial
tadalafil generic headache nausea cialis without prescription cialis maximum dose
cialis directions: TadalAccess – cialis canada free sample
cialis com coupons: cialis pill canada – cialis overdose
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis tablets
cialis 5 mg: Tadal Access – cialis male enhancement
india pharmacy cialis what is cialis pill cialis 20 mg tablets and prices
cialis where can i buy: Tadal Access – buy cialis no prescription australia
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis ingredients
cialis for sale in toront ontario: TadalAccess – buy cialis no prescription australia
sanofi cialis otc cheap cialis free shipping cialis for sale toronto
cialis walgreens: TadalAccess – tadalafil vidalista
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis tadalafil
cialis super active vs regular cialis: cialis 5mg coupon – does cialis make you harder
cialis is for daily use cialis back pain what does cialis look like
cialis san diego: price of cialis in pakistan – tadalafil tablets 20 mg global
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis and grapefruit enhance
order cialis online cheap generic: cialis pricing – does tadalafil work
canadian pharmacy cialis: Tadal Access – purchase cialis on line
https://tadalaccess.com/# pastillas cialis
what is the difference between cialis and tadalafil: Tadal Access – buying cheap cialis online
best research tadalafil 2017 Tadal Access buying cialis online usa
https://tadalaccess.com/# generic tadalafil canada
buying cheap cialis online: most recommended online pharmacies cialis – printable cialis coupon
buy cialis no prescription overnight: Tadal Access – buy cialis generic online
order generic cialis online cialis effects cialis paypal
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis available in walgreens over counter??
cheap cialis pills uk: Tadal Access – cialis brand no prescription 365
us pharmacy cialis: TadalAccess – generic tadalafil canada
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis tablets for sell
how much does cialis cost at walgreens cialis lower blood pressure how to buy cialis
viagara cialis levitra: TadalAccess – where to buy generic cialis ?
cialis super active real online store: TadalAccess – cialis walmart
https://tadalaccess.com/# tamsulosin vs. tadalafil
cialis super active reviews: tadalafil tablets 20 mg side effects – buy cialis usa
purchase brand cialis cialis efectos secundarios generic cialis from india
how much does cialis cost at walmart: Tadal Access – cialis stopped working
https://tadalaccess.com/# tamsulosin vs. tadalafil
canada pharmacy cialis: Tadal Access – cialis time
cialis online pharmacy buy liquid tadalafil online cialis professional
cialis trial pack: TadalAccess – cialis blood pressure
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis coupon online
mint pharmaceuticals tadalafil: TadalAccess – cialis buy online canada
cialis paypal buy cialis online without prescription tadalafil citrate powder
cialis and blood pressure: TadalAccess – cialis from canada to usa
https://tadalaccess.com/# buy cialis in canada
difference between sildenafil and tadalafil: cialis for daily use side effects – when to take cialis for best results
buy cialis canada paypal TadalAccess cialis 5mg how long does it take to work
cialis softabs online: mint pharmaceuticals tadalafil reviews – cialis las vegas
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis canada sale
cialis no prescription: Tadal Access – where to get the best price on cialis
how many mg of cialis should i take Tadal Access buy liquid tadalafil online
wallmart cialis: Tadal Access – cialis online aust
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis buy online canada
is tadalafil as effective as cialis: cialis samples for physicians – cialis 800 black canada
cialis difficulty ejaculating cialis side effects forum where to get the best price on cialis
buy cialis cheap fast delivery: TadalAccess – tadalafil liquid review
where can i get cialis: TadalAccess – cialis free
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis as generic
vigra vs cialis cialis 20mg tablets cialis price canada
what does cialis look like: TadalAccess – cialis generic best price
purchase generic cialis: TadalAccess – cialis prescription assistance program
https://tadalaccess.com/# cialis for bph reviews
how long for cialis to take effect Tadal Access how long does it take for cialis to start working
cialis buy online canada: cialis doesnt work for me – cialis for daily use
best time to take cialis 5mg: TadalAccess – tadalafil 40 mg with dapoxetine 60 mg
https://tadalaccess.com/# cheap cialis canada
Pharm Au24: Medications online Australia – Online medication store Australia
Ero Pharm Fast: Ero Pharm Fast – Ero Pharm Fast
https://pharmau24.shop/# Pharm Au24
Ero Pharm Fast: ed prescription online – ed online treatment
cheapest ed meds: ed prescription online – ed pills for sale
online pharmacy australia Discount pharmacy Australia pharmacy online australia
Ero Pharm Fast: where can i get ed pills – ed rx online
get ed prescription online: online prescription for ed – Ero Pharm Fast
Medications online Australia: Discount pharmacy Australia – pharmacy online australia
https://eropharmfast.com/# Ero Pharm Fast
cheapest online ed meds Ero Pharm Fast pills for ed online
wk1qur
yw4p7j
4gjt8q
zw0pst
oledbg
i0m02a
o02865
This design is incredible! You most certainly know how to keep a reader entertained. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Great job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
dohc2c
4vo76a
j0fe8x
helxov
Great post. I’m facing many of these issues as well..
Статья представляет несколько точек зрения на данную тему и анализирует их достоинства и недостатки. Это помогает читателю рассмотреть проблему с разных сторон и принять информированное решение.
great points altogether, you just received a brand new reader. What might you suggest about your post that you made some days in the past? Any sure?
Эта статья является настоящим источником вдохновения и мотивации. Она не только предоставляет информацию, но и стимулирует к дальнейшему изучению темы. Большое спасибо автору за его старания в создании такого мотивирующего контента!
tiqvxo
Автор предлагает практические рекомендации, которые могут быть полезны в реальной жизни для решения проблемы.
Статья содержит информацию, подкрепленную надежными источниками, представленную без предвзятости.
Эта статья оказалась исключительно информативной и понятной. Автор представил сложные концепции и теории в простой и доступной форме. Я нашел ее очень полезной и вдохновляющей!
Статья представляет обширный обзор темы и учитывает ее исторический контекст.
Автор представляет сложные понятия в доступной форме, что помогает лучше понять тему.
Я оцениваю использование автором разнообразных источников, что позволяет получить всестороннюю информацию.
Hello just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The text in your article seem to be running off the screen in Internet explorer. I’m not sure if this is a format issue or something to do with browser compatibility but I thought I’d post to let you know. The style and design look great though! Hope you get the issue fixed soon. Cheers
Автор старается представить информацию в объективной манере, оставляя пространство для дальнейшего обсуждения.
v86csv
Автор старается оставаться нейтральным, предоставляя информацию для дальнейшего изучения.
rz5pjg
2wi2t8
pgsmu0
osnq26
В современном мире, где онлайн-присутствие становится все более важным для бизнеса, повышение видимости и ранжирования сайта в поисковых системах является одной из самых важных задач для веб-мастеров и маркетологов. Одним из основных факторов, влияющих на рост авторитетности сайта, является его DR (Domain Rating), который определяется в основном путем анализа ссылочной массы сайта.
Я оцениваю четкую структуру статьи, которая помогает организовать мысли и понять ее содержание.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I have recently started a website, the information you provide on this website has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work. “‘Tis our true policy to steer clear of permanent alliances with any portion of the foreign world.” by George Washington.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
6a19vg
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
I really like your writing style, great info , thanks for putting up : D.
94b1y3