Terminologies Used in Digital Advertising: A Comprehensive Guide
Digital advertising has become an integral part of marketing strategies across industries. To navigate the vast landscape of digital advertising, it is essential to understand the basic terms and concepts used in this domain. Whether you are a marketer, business owner, or simply curious about the world of digital advertising, this article will provide you with a comprehensive guide to the fundamental terms you need to know.
The following explanations of the most common digital advertising terms will help you navigate the world of online advertising.
301 Redirect: Some technical terms are critical for digital marketers to understand. This is one of them. When you move a page to a new URL, you need to instruct search engines such as Google and Bing on how to treat that move. A 301 redirect lets search engines know that you permanently moved your content to a new URL. Searchers will automatically be redirected.
404 Error: This error code indicates that the requested page could not be found by the server, even though the browser established communication with the relevant server. If one of your pages generates a 404 Error, you need to check what’s happening because there’s bound to be some technical error.
A
A/B Testing: A method used to determine which version of an ad or landing page performs better. A/B tests involve running two versions simultaneously while changing only one element at a time to pinpoint the key variable that drives audience response. Once a winner is identified, it becomes the next control and is compared with another version for further testing and optimization.
Above the Fold: This term originated in print advertising, referring to the top half of a newspaper where the most prominent headlines were placed. In a digital context, it describes the part of a web or landing page that’s visible without scrolling down. To maximize conversions, landing page best practices suggest placing your most important message and CTA above the fold. Keep in mind that there’s no standard pixel size for the fold, as it depends on the user’s screen size and resolution.
Account-Based Advertising: One tactic in an account-based marketing (ABM) strategy, account-based advertising displays ads exclusively to specific job titles at your target accounts. For instance, if you want to market a new food packaging product to General Mills, you can target individuals with titles such as Senior Product Manager, Senior Product Marketer, or VP of Product Marketing. This ensures that your ads are only visible to the relevant people at General Mills.

Ad Audience: The overall number of individuals who have either already seen or could potentially see an ad during a specific period.
Ad Banner: One of the most common forms of digital advertising. These ad units can include static graphics, videos, and/or interactive rich media, and are displayed on web pages or in applications.
Ad Click: The action that occurs when a user interacts with an ad by either clicking on it with their mouse or pressing enter on their keyboard.
Ad Exchange: An online marketplace that enables publishers and advertisers to buy and sell advertising inventory in real-time auctions. Unlike historical methods of buying ad inventory that involved price negotiations for ad placements on specific websites, ad exchanges enable instantaneous bidding for ad space available across the internet.
Ad Formats: A specification for advertising creative that often includes whether the ad will contain text, audio or graphical content, the size of the creative and the web-enabled device used to view the creative. The Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) has defined standard ad formats, there are also native formats which are custom to a site.
Ad Impressions: The number of times an ad is displayed or shown to a user’s screen, regardless of whether the user has actually seen or interacted with the ad in any way. (Also see: Ad Serving)
Ad Inventory: The total amount of advertising space or impressions a digital publisher can sell. For example, if The Gotham Times averages 1,000 visits to its homepage in any given week, and they have space for two display ads on its homepage, then its potential ad inventory is 2,000 impressions per week.
Ad Network: A vendor that connects advertisers to publishers, typically by aggregating ad inventory across multiple publishers and offering it to advertisers as a single point of contact.
Arbitrage: Paying publishers on one metric (e.g., CPM) and selling to buyers on another metric (e.g., CPC) to improve one’s margin, while reducing risk to buyers – they only pay for what they wanted (clicks in this example).
Ad Serving: The delivery of an ad from a web server to the end user’s device, where the ads are displayed on a browser or an application.
Ad Targeting: The process of displaying ads to a specific group of people based on demographic, geographical, psychographic, or behavioral data.
Ad Tech: Ad tech, short for “advertising technology”, are technology services that provide marketers with the ability to engage people across digital properties to achieve marketer-specified outcomes (e.g., brand awareness, engagement, consideration, conversion) and provide media owners selling & yield tools to better monetize their inventory.
Attribution: Marketing attribution is how marketers assign credit for the success of their advertising campaigns. It evaluates the marketing touchpoints a consumer encounters on their path to a desired outcome (such as purchase). The goal of attribution is to determine which channels and messages had the greatest impact on the decision to take the desired action (such as click or conversion).
Ad Units: Specific, standardized spaces on a website or app to place an ad. The Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB), a trade association promoting digital ad standards and practices, maintains a set of guidelines for sizing and formatting different types of ad units.
Addressable: The ability to target individual users or devices based on demographic or behavioral data with relevant and personalized ads.
Affiliate Marketing: A type of performance-based marketing in which advertisers compensate promotional partners for driving traffic to their products or services, based on clicks or sales.
B
Banner Ad: An online creative placed on a media owner’s digital property (e.g., a publisher’s webpage). A traditional display banner usually has a preset size (e.g., 300X250 pixels) and often includes a combination of images and text.
Behavioral Targeting: Behavioral Targeting, also known as Online Behavioral Targeting (OBA) or Interest-based Advertising, generates an attribute from a consumer’s prior activity, such as the number of pages visited about a particular topic or interactions with content (including ad clicks) associated with a particular brand.
Bidding strategy: The way a buyer determines how much they’re willing to pay for ad placement in an auction. For example, an advertiser could choose to bid a flat rate, bid based on the expected clickthrough rate, or use past performance data. A successful bidding strategy wins the ad placement while optimizing the ROI for the buyer.
Blocklist: A list of websites that an advertiser does not want their ads to appear on, usually when a brand wants to avoid association with controversial or inappropriate content. Blocklists can also include keywords or products to exclude from campaigns.
Bounce Rate: The percentage of website visitors that only look at one page before navigating away from the site. High bounce rates often indicate that visitors aren’t finding what they’re looking for, or that the site or landing page has poor design or usability.
Brand Awareness: The level of consumer recognition or recall for a particular brand or product. In addition to conversions, increased brand awareness is a typical goal and measure of success for marketing campaigns.
Browser: A software application used to access and display content on the World Wide Web. The most popular web browsers include Google’s Chrome, Apple’s Safari, Microsoft’s Edge, Mozilla’s Firefox, and Opera.
C
Call to Action (CTA): An active invitation included within an ad or on a landing page that guides a user to take a certain action. Commonly used CTAs include Buy Now, Sign Up, Download the Whitepaper, Get Started, and Read More.
Campaign: A set of creative, budget and engagement tactics a marketer configures in Criteo DSP to achieve an outcome, measured by a pre-determined set of metrics.
Capping: Frequency capping means restricting (capping) the number of times (frequency) a specific visitor is shown a particular ad.
Channel: In digital advertising, channels are specific platforms businesses use to reach their target audience. Digital ad channels include display ads, social media, email, and mobile in-app advertising.
Click-through Rate (CTR): A metric that shows how often people who are served an ad actually click on it. Expressed as a percentage of total impressions, an ad’s CTR is calculated by dividing the number of clicks an ad received by the number of times it’s been served. For example, if an ad received 5 clicks and was shown 1000 times, the CTR is 0.5%. The higher the CTR on an ad, the better it’s performing.
Connected TV (CTV): A device where ads are served within shows and movies that are streamed via over-the-top (OTT) services on any connected TV (televisions with a built-in internet connection) or streaming devices (like Apple TV, Amazon Firestick or Roku).
Consent management platform (CMP): A tool publishers use to request, manage, store, and update users’ consent related to data processing and privacy. For users, CMPs usually include an easy interface to control how their data is collected, used, and shared. For publishers, CMPs enable compliance with privacy regulations and laws.
Conversion: An action that advertisers want their audience to take. When launching a campaign, advertisers select a specific action or set of actions, and when an audience member takes this action, it’s counted as a conversion. Common examples of conversions include making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or requesting a demo.
Conversion Pixel: A 1×1 image pixel, usually transparent and invisible to users, that is embedded into a web page (such as a thank-you page) and triggered whenever a conversion occurs.
Conversion Rate: A metric that reflects the percentage of users who take a desired action. Conversion rates are calculated by dividing the number of conversions (such as purchases or form fills) by the number of views or visits, then converting to a percentage.

Understanding digital advertising terms like conversion rate is key to success for marketers.
Conversion rate optimization (CRO): The process of improving the percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action, such as filling out a form or making a purchase. CRO is achieved by using tactics like A/B testing and user testing to identify and make changes to messaging, graphics, CTAs, and other elements on a page to improve user experience and increase conversions.
Conversion Tracking: Monitoring how many conversions have occurred during any specific time period, and analyzing which ads led to the conversions.
Cookie: A small text file that advertisers use to track how visitors interact with a website and remember user behavior and preferences. (See also first-party cookies and third-party cookies.)
Cost per Acquisition (CPA): The cost of acquiring one customer. CPA is typically calculated by dividing the total amount spent on an advertising campaign by the number of customers acquired through that campaign.
Cost per Click (CPC): How much an advertiser pays, on average, for each ad click. CPC is calculated by dividing the total amount spent on a campaign by the number of clicks generated.
Cost per Completed View (CPCV): A pricing model that determines how much an advertiser pays when a video ad is viewed to completion. As opposed to paying per impression, the CPCV model only charges the advertiser when a viewer watches the entire ad.
Cost per Lead (CPL): How much an advertiser pays, on average, for each ad click that results in a lead conversion. CPL is calculated by dividing the total amount spent on a campaign by the number of leads generated.
Cost per Mille (CPM)/Cost per Thousand: How much does it cost to serve 1,000 ad impressions. CPM is used as a standard measure for buying display ads. (Fun fact, mille means “thousand” in Latin.)
Cross-Device Targeting: A strategy that enables advertisers to reach the same buyer with targeted ads across multiple devices, such as tablets, desktops, or smartphones.
Contextual Targeting: A digital ad strategy that involves displaying ads to users based on the content of the webpage they’re currently viewing (as opposed to user data). For example, an airline would place an ad on a travel article while a flour brand would advertise on a baking site.
D
Data Management Platform (DMP): Software-based solution that aggregates and processes data feeds that provide insights into audiences and targeting for buyers and sellers of ads.
Deal ID: A Deal Identifier is a unique number that usually consists of 19 characters and is generated by the publisher’s supply-side platform (or an ad server) for a programmatic direct deal (i.e. private auctions for private marketplaces, or preferred deals, or guaranteed deals). Deal ID enables media buyers to identify publishers in the auction and buy their premium inventories based on certain pre-negotiated terms.
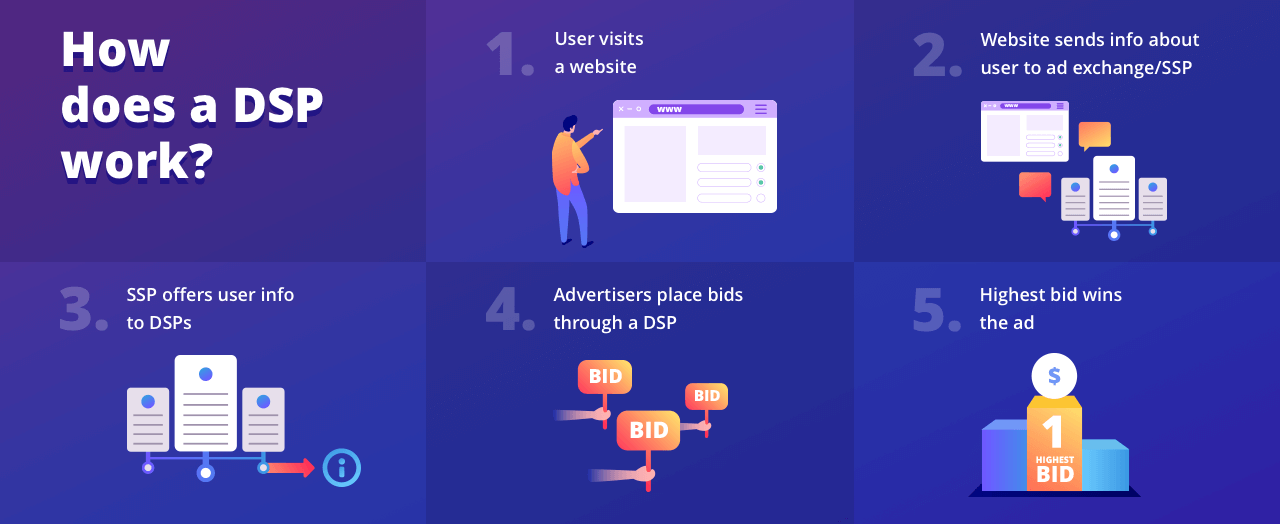
Demand-Side Platform (DSP): A technology platform that allows advertisers to buy ad space across multiple ad exchanges, ad networks, and other sources through a single interface. DSPs use automation to target specific users and optimize campaigns based on user data.
Direct Response (DR): A digital advertising term describing a campaign or ad specifically created to encourage audiences to take immediate action.
Display Advertising: A digital advertising format where graphic ads are shown on a web page. The term originated in newspapers, and the principles still apply. Display ads can be graphics, videos, interactive images (a quiz or a game), and expandable.
Dynamic Ads: An ad automatically personalized for the consumer viewing it in order to create additional engagement and conversions.
Dynamic Creative: Responsive ad type that leverages the product catalog to dynamically optimize the content and messaging, delivering a personalized experience to each consumer.
E
Effective Cost Per Mille (ECPM): A relevant KPI selected by the advertiser (CTR/CR/COS) divided by impressions delivered, regardless of the pricing model used to purchase the impressions (CPM, CPC, CPA, CPL, CPCV, etc). Example for a typical CPC charging model: eCPM = (CPC x clicks / impressions) x 1000.
Email Advertising: Clickable banner ads, sponsored articles, and links that appear within emails and e-newsletters.
F
First-party cookies: Small data files, or cookies, that are created and controlled by a website to store user preferences, log-in status, and other settings. (See also Cookies and Third-party Cookies.)
First Party Data (1P DATA):First-party data is information that a company can collect from their own sources. Usually, information about customers from both online and offline sources, such as the company’s website, app, CRM, social media or surveys is first party data.
First-touch: An attribution model that gives 100% of the credit for a conversion to the first touchpoint in a user’s journey.
Frequency Capping: The practice of setting a limit on the number of times an ad should be shown to a consumer within a specific timeframe (such as a week or month).
Full-Funnel Marketing: A strategy that addresses the full shopper journey and incorporates objectives for all stages of the purchase funnel: awareness, consideration, and conversion.
G
Geographic Targeting: Selecting an audience for a campaign based on zip codes, designated marketing area (DMA), cities, states, and countries.

GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): The European Union’s landmark 2018 privacy act that protects its citizens by regulating how companies collect and process their personal data (even if the company isn’t based in the EU).
Guaranteed Deal: A type of programmatic deal based on a guaranteed volume of impressions sold at a fixed price and for a guaranteed budget.
H
HTML: An acronym for Hypertext Markup Language (HTML), which is the coding language for rendering interactive content on open web.
I
Identity Graph (ID Graph): A database that connects different signals associated with a single user or device across multiple platforms, including cookies, device IDs, social media accounts, and email addresses.
Impression (Or Display): An opportunity to serve an ad to a consumer on a digital device.
In-Stream Video Ads: Video ads are played before, during, or after the video content the publisher is delivering to the consumer.
Interstitial Ads: Ads that appear at natural transition points in the flow of an app, such as between activities or during the pause between levels in a game. It is usually displayed as a full-screen pop-up ad. For example, when a user navigates to a mobile website, that brand might offer an interstitial ad for their mobile app.
Insertion Order (IO): The contract signed by an advertiser/agency to validate a new budget for an advertising campaign. It is signed by the advertiser.
Interactions: Touchpoints of when a consumer sees, clicks, visits a store, or other activity related to the marketing and monetization efforts of our customers.
Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB): A trade body organization that helps sets standards and guidelines for digital advertising.
Inventory Management: A process used by media owners to package and monetize the ad space in their digital properties.
K
Key Performance Indicator (KPI): The target or result that you want to achieve. In other words, it’s how you measure the success of a campaign. Common KPIs are ROAS, COS, and CPL and CPV .
Keyword: A specific word or phrase that advertisers select to trigger and include paid search ads or contextual ads. (Hint: every digital marketing term in this article is a potential keyword). In search advertising, the highest bidder on a keyword usually gets the top position.
Keywords Tag: META tag used to help define the primary keywords of a Web page.
L
Landing Page: A standalone web page where users reach after they click on a link within an email, display ad, paid search, or other conversion paths.
Last-touch/Last click: An attribution model that gives 100% of the credit for a conversion to the last touchpoint in a user’s journey.
Lead: A potential customer. In digital advertising, a lead is an individual who gives you their contact information by signing up for a newsletter or filling out a form.
Lookalike Audience: A target audience that shares similar demographics, interests, behaviors, or other attributes with your existing customer base. Advertisers can target lookalike audiences on digital advertising platforms, including Facebook and LinkedIn, with the goal of reaching people who are likely to be interested in their products or services.
Lookback Window: A specific timeframe (hours, days, weeks, or months) advertisers set and use for conversion attribution or other time-sensitive reporting or goals.
M
Media Plan: Media planning is the process by which marketers determine who to engage, where to reach them, when to message, and how frequently to maximize engagements and ROI.
Mobile Ads: Standardized ad units designed for mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets.
Mobile Advertiser ID (MAID): A unique identifier assigned to a mobile device by its operating system (like Android or iOS). Advertisers use MAIDs to track and target mobile users with personalized ads, but users can choose to reset and clear their mobile advertising data at any time.
Monetization: Monetization is the process of turning an asset into revenue, for Media Owners this can be ad space on their digital properties, their data or converting visitors into customers.
Multi-channel attribution: An attribution model that weighs each touchpoint along a buyer’s journey, across channels and devices.
N
Native Advertising: A paid ad that matches the form of its surrounding user experience and content, such as a sponsored magazine article or a social media post. Native ads are intended to feel seamless, organic, and valuable, rather than sticking out as a blatant advertisement.
O
Omnichannel Retail: Refers to a retail environment selling products across online and offline channels and creating a consistent customer experience across those sales channels. Typical channels include online retailers, marketplaces, social channels and brick-and-mortar stores.
Online Video (OLV): OLV is a video ad format commonly referred to in reference to video advertising on web and mobile app devices (as opposed to Connected TV devices).
Opt-Out: A user-signaled preference to no longer receive behaviorally targeted ads. Users can opt-out of receiving behaviorally targeted ads from Criteo on or our Privacy page after clicking on the blue ‘i’ icon on each Criteo banner.
Over-The-Top (OTT): OTT is any video content “over the top of a cable box”. It is an umbrella term that includes both CTV and OLV advertising. Includes services such as Netflix, Hulu, and Sling.
Overlay: A decreasingly utilized digital ad format that “floats” over a webpage, video, or app content.
P
Paid Search: Ads that appear within search engine results pages, based on targeted keywords included in the search queries.
Passback: A media owner’s ability to repurpose an unfilled impression as a buying opportunity for the next buyer in their waterfall. This is an antiquated and largely inefficient way of running a media owner ad stack, but still exists today.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC): A pricing model where advertisers pay vendors or publishers based on the number of clicks received in a campaign. PPC is the most common model of paid search advertising.
Personally Identifiable Information (PII): A legal term for any data that can be used to distinguish the real-world identity of a user, including (but not limited to) names, addresses, ID numbers, phone numbers, and birthdates.
Pop Ads: Pop-up and pop-under ads are ads that open in a new browser window, either “over” or “under” the current window. Pop-up ads in particular are typically viewed as annoying and a poor user experience, and many browsers block them by default.
Premium Ad Inventory: Ad inventory that is considered to be of high quality and is therefore valued at a higher price.
Private Marketplace (PMP): A Private Marketplace (PMP) refers to the real-time auction of publishers’ ad inventory in an invite-only setup with a selected number of advertisers. PMP is an invite-only auction where a publisher invites advertisers to bid on its inventory. Due to this “invite-only” feature, this auction is termed as a private auction.
Programmatic Advertising: A method of buying ad space that uses automation and AI to enable marketers to target an audience, set a budget, place real-time bids, and purchase advertising from a publisher. Programmatic advertising uses data to make decisions about which ads to buy in real-time, which improves efficiency and increases the effectiveness of the ads. (See also, Ad Exchange.)
Publisher: A website that publishes content (news, etc.) and which often monetizes its traffic by selling ad placements.
R
Reach: Share of the marketer’s audience exposed to at least one ad.
Real-time bidding (RTB): A method of buying and selling ad impressions in real-time auctions through programmatic platforms. RTB takes place in milliseconds, on an impression-by-impression basis, with the goal of increasing ad buying efficiency and using real-time data to decide which ad to show to which user.
Retargeting/Remarketing: Serving ads to people who have previously visited your website.
Return on Advertising Spend (ROAS): This metric shows how much revenue is generated for every dollar of ad spend, and is expressed as a ratio (such as 2:1).
Return on Investment (ROI): Digital marketing ROI is usually calculated as Revenue/Cost. Cost usually means initial investment, but also cost of an ad campaign. ROI = 1/COS. In many cases, ROI is equivalent to Return on Ad Spend (ROAS).
Rich Media: Unlike static banner ads, this type of advertising incorporates advanced features such as video, audio, or interactive quizzes and games to improve engagement and provide an immersive experience.
S
Sales: When a consumer makes a purchase of the desired product or service.
Social Advertising: Running paid ads on online social networking platforms, such as Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter.
Supply Side Platform (SSP): A supply-side platform (SSP) is a software system that allows publishers to offer their available inventory to ad exchanges and demand-side platforms (DSP)s.
T
Third-party Cookies: Small data files, or cookies, that are set by domains other than the one the user is currently visiting. Often used for tracking and advertising purposes, third-party cookies are being increasingly restricted by government regulations and tech platforms to protect user privacy. (See also Cookies and First-party Cookies.)
Third Patry Data (3P DATA): Data sold by a partner. 3P data is used to enhance and scale audiences.
U
Unique Visitor: Counting website visitors on a unique level. When a person visits a site or app, the individual is counted once, no matter how many times or pages the person visits, thus creating a better idea of how many people are visiting.
User: An individual with access to the Internet. A user can access the Internet through multiple browsers or devices, and thus have multiple cookies/user IDs.
User ID: A token attributed to a technical identifier, such as a cookie or device ID, and specific to a given browser or device.
V
Video Completion Rate (VCR): VCR is a widespread KPI for video campaigns, expressed as a percentage. It is the ratio between the number of completed views and the number of exposed consumers. Usually, a consumer must watch a minimum duration on the video ad for it to count as a completed view.
View-Through: An attribution metric used to reflect the number of times a user views an ad without clicking, but later converts. View-throughs are a way to track the effectiveness of an ad that may have influenced a customer’s decision, even if they didn’t directly interact with that ad. View-through windows typically define the number of days after viewing an ad that the consumer’s relevant actions within that time period can be attributed to the ad.
Visit: When a consumer who has seen an advert goes to the desired pages or store to get more information.
Y
Yield: Ad yield is the amount of revenue you earn from your ads. In other words, it is an indicator of how successful your advertising efforts were.
Understanding the basic terms of digital advertising is essential for anyone involved in marketing or advertising. These terms provide a foundation for measuring the success and effectiveness of ad campaigns. By familiarizing yourself with these terms, you can make informed decisions, optimize your campaigns, and drive better results in the dynamic world of digital advertising.

Профессиональный сервисный центр по ремонту бытовой техники с выездом на дом.
Мы предлагаем:ремонт бытовой техники в мск
Наши мастера оперативно устранят неисправности вашего устройства в сервисе или с выездом на дом!
j7q6d0
vibracion de motor
Equipos de equilibrado: esencial para el rendimiento estable y eficiente de las maquinarias.
En el ambito de la tecnologia moderna, donde la rendimiento y la seguridad del sistema son de alta trascendencia, los aparatos de equilibrado desempenan un rol vital. Estos dispositivos dedicados estan concebidos para ajustar y estabilizar piezas rotativas, ya sea en equipamiento productiva, automoviles de desplazamiento o incluso en electrodomesticos hogarenos.
Para los especialistas en conservacion de aparatos y los ingenieros, utilizar con dispositivos de calibracion es crucial para asegurar el operacion suave y fiable de cualquier aparato rotativo. Gracias a estas soluciones modernas innovadoras, es posible limitar considerablemente las sacudidas, el estruendo y la esfuerzo sobre los soportes, mejorando la vida util de componentes importantes.
Asimismo importante es el rol que cumplen los sistemas de ajuste en la servicio al comprador. El soporte tecnico y el soporte permanente utilizando estos sistemas facilitan ofrecer soluciones de optima excelencia, elevando la bienestar de los usuarios.
Para los titulares de empresas, la inversion en equipos de equilibrado y dispositivos puede ser importante para mejorar la efectividad y desempeno de sus equipos. Esto es particularmente importante para los duenos de negocios que administran medianas y pequenas organizaciones, donde cada detalle vale.
Asimismo, los dispositivos de balanceo tienen una vasta implementacion en el area de la proteccion y el monitoreo de calidad. Facilitan encontrar eventuales fallos, previniendo intervenciones costosas y averias a los dispositivos. Mas aun, los indicadores obtenidos de estos dispositivos pueden usarse para mejorar sistemas y mejorar la presencia en sistemas de busqueda.
Las areas de aplicacion de los aparatos de balanceo abarcan variadas sectores, desde la fabricacion de ciclos hasta el control ecologico. No importa si se trata de enormes fabricaciones de fabrica o modestos locales domesticos, los equipos de calibracion son fundamentales para asegurar un operacion optimo y libre de interrupciones.
qrmqfq
lypyqa
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
bue8dg
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
uvr5ww
Someone essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the very first time I frequented your website page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to create this particular publish incredible. Fantastic job!
7jolb7
exxflq
l53soh
vp5atj
zgz4ju
i4zecm
Автор статьи предоставляет факты и аргументы, не влияя на читателя своими собственными предпочтениями или предвзятостью.
Это позволяет читателям формировать свое собственное мнение на основ
Надеюсь, что эти комментарии добавят ещё больше положительных настроений к информационной статье! Это сообщение отправлено с сайта GoToTop.ee
vztjly
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright infringement? My blog has a lot of exclusive content I’ve either created myself or outsourced but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the web without my permission. Do you know any techniques to help reduce content from being ripped off? I’d truly appreciate it.
Great post. I used to be checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed! Very helpful info specially the ultimate section 🙂 I deal with such info much. I used to be seeking this certain info for a very lengthy time. Thanks and best of luck.
Статья предлагает глубокий анализ темы и рассматривает ее со всех сторон.
Thank you for the good writeup. It if truth be told was a enjoyment account it. Glance complex to far added agreeable from you! However, how could we communicate?
Читателям предоставляется возможность ознакомиться с фактами и самостоятельно сделать выводы.
wdy2yb
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
hqh0it
Why users still use to read news papers when in this technological globe everything is presented on web?
x19ohx
Хорошая работа по анализу проблемы и представлению различных точек зрения.
I am now not positive where you are getting your info, however great topic. I must spend some time studying more or working out more. Thank you for fantastic info I was on the lookout for this info for my mission.
hko3wg
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
Мне понравился четкий и структурированный стиль изложения в статье.
I think this is among the most vital info for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But wanna remark on few general things, The web site style is great, the articles is really nice : D. Good job, cheers
What’s Happening i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & aid other users like its helped me. Great job.
hatuf9
ghnf1c
8gsabb
vrg9hj
Читателям предоставляется возможность самостоятельно интерпретировать представленную информацию.
Some times its a pain in the ass to read what website owners wrote but this web site is very user friendly! .
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..extra wait .. …
Статья содержит информацию, подкрепленную надежными источниками, представленную без предвзятости.
Greetings! Very helpful advice within this article! It’s the little changes that produce the biggest changes. Many thanks for sharing!
Woh I love your content, saved to fav! .
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://www.binance.info/en-IN/register-person?ref=UM6SMJM3
zl7ka5
d2h8hw
q0u55v
Это позволяет читателям формировать свою собственную точку зрения на основе фактов.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Looking through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I will forward this information to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. I appreciate you for sharing!
Автор представляет информацию в организованной и последовательной форме, что erleichtert das Verständnis.
Hello, constantly i used to check webpage posts here early in the break of day, for the reason that i like to learn more and more.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thanks , I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your website?
Информационная статья представляет различные аргументы и контекст в отношении обсуждаемой темы.
o453hz
I was wondering if you ever considered changing the layout of your blog? Its very well written; I love what youve got to say. But maybe you could a little more in the way of content so people could connect with it better. Youve got an awful lot of text for only having 1 or two images. Maybe you could space it out better?
Hello There. I found your blog the usage of msn. This is a very well written article. I will be sure to bookmark it and come back to learn extra of your helpful info. Thanks for the post. I’ll certainly comeback.
Статья представляет информацию о текущих событиях, описывая различные аспекты ситуации.
The other day, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a twenty five foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My iPad is now destroyed and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
1xamav